Embark on a journey into the realm of Radius servers, where networking and security converge to enhance connectivity and protect data. From authentication to configuration, this topic delves into the intricacies of Radius servers, shedding light on their importance and functions in a network environment.
Overview of Radius Server
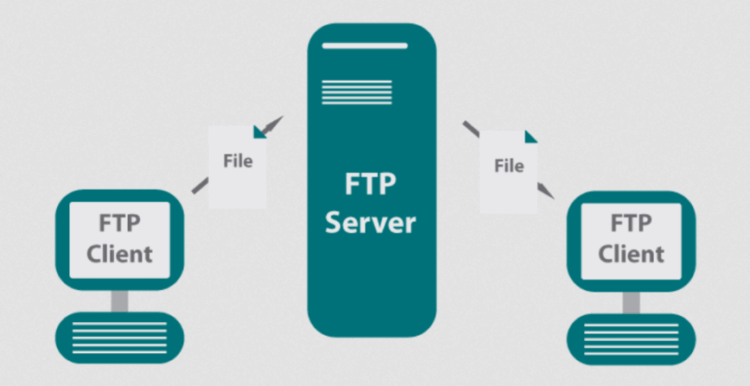
A Radius server, which stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is a networking protocol that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting management for users connecting to a network. Its primary purpose is to secure and control access to the network by verifying the credentials of users and granting appropriate levels of access based on predefined policies.Scenarios of Common Usage
- Wireless Networks: Radius servers are commonly used in Wi-Fi networks to authenticate users before allowing them access to the network.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Radius servers play a crucial role in VPNs by authenticating remote users before granting them access to the private network.
- Enterprise Networks: In organizations, Radius servers are utilized to manage user access to resources like servers, databases, and applications.
Basic Functions of Radius Server
- Authentication: The Radius server verifies the identity of users attempting to access the network by checking their credentials such as usernames and passwords.
- Authorization: Once authenticated, the Radius server determines the level of access the user is allowed based on predefined policies and permissions.
- Accounting: The Radius server keeps track of user activity, including logins, logouts, data usage, and other network-related actions for auditing and billing purposes.
Radius Server Authentication
The authentication process used by a Radius server involves verifying the identity of a user or device before granting access to a network. This helps ensure that only authorized individuals can connect to the network and access its resources securely.Types of Authentication Protocols
- RADIUS supports a variety of authentication protocols, including PAP (Password Authentication Protocol), CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol), EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol), and more.
- These protocols allow for different methods of authentication, such as using passwords, digital certificates, tokens, or biometrics, depending on the security requirements of the network.
Role of Encryption in Securing Authentication Data
Encryption plays a crucial role in securing authentication data within a Radius server by protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or interception.- When a user sends their credentials to the Radius server for authentication, the data is encrypted to prevent eavesdropping or tampering during transmission.
- Encryption ensures that passwords and other authentication details are securely stored and transmitted, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to the network.
Radius Server Configuration
Configuring a Radius server involves several key steps to ensure proper operation. Setting up the necessary parameters is crucial in customizing the server to meet specific requirements.Configuring Parameters
- Shared Secret: This is a key parameter that must be set up between the Radius server and the client to authenticate communication. It should be a complex string of characters for security.
- Authentication Protocols: Radius supports various authentication protocols such as PAP, CHAP, and EAP. These protocols need to be configured based on the network's security policies.
- Network Access Server (NAS) Configuration: Define the NAS devices that will communicate with the Radius server. Each NAS device should have its own configuration settings.
- User Access Control: Configure access policies for users based on attributes such as username, password, and group membership.
Customization Examples
- Session Timeout: Set the duration of a user session before automatic logout.
- Accounting: Enable/disable accounting for monitoring user activities and resource usage.
- Authentication Port: Define the port through which authentication requests will be received.
- Logging: Configure logging levels to track server activities and troubleshoot issues.
Integration with Network Devices
When it comes to integrating a Radius server with network devices, it plays a crucial role in providing centralized authentication for users accessing the network. This integration allows for a seamless and secure way to manage user access and permissions across various devices within the network infrastructure.Advantages of Using a Radius Server for Centralized Authentication
- Centralized Management: A Radius server enables centralized user authentication, authorization, and accounting, making it easier to manage user access across multiple network devices.
- Enhanced Security: By using a Radius server, organizations can implement stronger security measures such as two-factor authentication, ensuring secure access to network resources.
- Scalability: Radius servers are highly scalable, allowing organizations to easily expand their network infrastructure without compromising on security or performance.
- Audit Trails: Radius servers provide detailed audit trails of user activities, helping organizations track and monitor user access for compliance and security purposes.
Examples of Network Devices Leveraging a Radius Server
- Wireless Access Points: Devices such as Wi-Fi routers and access points can leverage a Radius server for user authentication, allowing for secure access to wireless networks.
- VPN Gateways: Virtual Private Network (VPN) gateways can integrate with a Radius server to authenticate remote users connecting to the corporate network securely.
- Switches and Routers: Network switches and routers can use a Radius server for authenticating users accessing the network through wired connections, ensuring only authorized users gain access.
Radius Server Security
Securing a Radius server is crucial to protect sensitive network information and prevent unauthorized access. Implementing security best practices can help mitigate potential risks and ensure the integrity of the authentication process.Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms
- Use strong passwords: Encourage users to create complex passwords that include a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Implement an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a second factor such as a token or biometric scan.
- Regularly update credentials: Enforce password expiration policies to ensure that outdated credentials are not compromised.
Encrypt Data Transmission
- Use TLS/SSL encryption: Secure communication between the Radius server and network devices by enabling Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption.
- Implement IPsec VPNs: Establish secure VPN connections to encrypt data transmitted over the network, protecting sensitive information from interception.
Access Control Measures
- Implement role-based access control: Assign specific roles and permissions to users based on their responsibilities to limit unauthorized access to critical network resources.
- Monitor and audit user activity: Keep track of user logins, authentication attempts, and system changes to detect suspicious behavior and potential security breaches.