Starting with Microsoft IIS, we delve into its intricacies and functionalities, shedding light on its role in the realm of web hosting. Get ready for a journey through the evolution of this powerful web server technology.
Delving deeper, we uncover the key aspects that make Microsoft IIS a standout player in the web hosting arena.
Overview of Microsoft IIS
Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) is a web server software created by Microsoft for use with the Windows NT family of operating systems. Its primary function is to serve web pages and applications to users over the internet or an intranet.Brief History of Microsoft IIS
Microsoft IIS was first released in 1995 as part of the Windows NT 3.51 Service Pack 3. Over the years, it has undergone several updates and improvements to keep up with the evolving web technologies and security standards.Significance of Microsoft IIS
- Microsoft IIS is popular among enterprises and businesses that use Windows servers, as it integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products and services.
- It offers strong support for ASP.NET, Microsoft's server-side web application framework, making it a preferred choice for hosting ASP.NET applications.
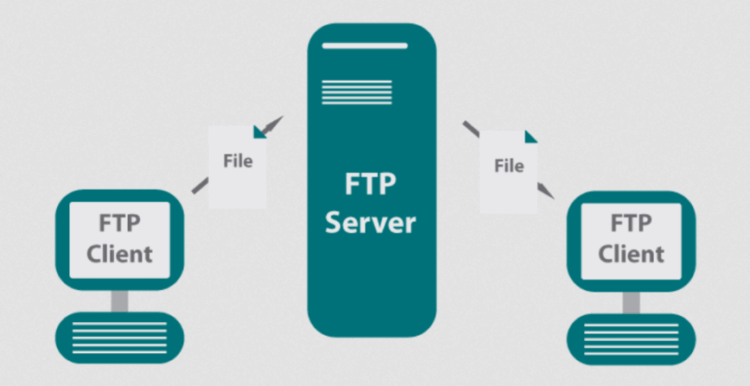
- With features like SSL/TLS encryption, URL rewriting, and FTP support, Microsoft IIS provides a secure and reliable platform for hosting websites and web applications.
Features of Microsoft IIS
Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) offers a range of features that make it a popular choice for hosting websites and web applications. These features contribute to its overall performance and usability.Scalability and Performance
- Microsoft IIS is known for its scalability, allowing websites to handle large amounts of traffic without sacrificing performance.
- It offers support for multiple processors and cores, ensuring efficient utilization of hardware resources.
- The built-in caching mechanisms help improve response times and reduce server load, enhancing overall performance.
Security Features
- IIS provides various security features, including SSL encryption, request filtering, and IP address restrictions, to protect websites from potential threats.
- Integration with Windows authentication mechanisms offers secure access control options for websites and applications.
- Regular security updates from Microsoft help address vulnerabilities and ensure the system remains secure.
Management Tools
- The IIS Manager provides a user-friendly interface for configuring and managing websites, application pools, and server settings.
- Integration with Microsoft Azure allows for seamless deployment and management of web applications in the cloud.
- Powerful diagnostic tools, such as logging and tracing features, help troubleshoot issues and monitor server performance.
Extensibility and Compatibility
- IIS supports a wide range of programming languages, frameworks, and technologies, making it versatile and compatible with various types of web applications.
- Modules and extensions can be easily added to customize the server's functionality based on specific requirements.
- Integration with other Microsoft products, such as SQL Server and ASP.NET, ensures seamless operation and enhanced capabilities.
Installation and Configuration
To install Microsoft IIS on a Windows server, follow these steps:Installation Steps
- Open Server Manager on your Windows server.
- Click on "Add roles and features."
- Select the Web Server (IIS) role and click Install.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Configuration of Websites, Virtual Directories, and Application Pools
To configure websites, virtual directories, and application pools in Microsoft IIS, you can follow these guidelines:- Open IIS Manager on your Windows server.
- For websites, right-click on Sites and choose Add Website. Fill in the necessary details like site name, physical path, and port number.
- For virtual directories, right-click on the site where you want to add the virtual directory and choose Add Virtual Directory. Specify the alias and physical path.
- For application pools, go to Application Pools in IIS Manager and create a new application pool. Configure settings such as .NET CLR version, Managed pipeline mode, and start mode.
Tips for Performance Optimization
To optimize performance through configuration settings in Microsoft IIS, consider the following tips:- Enable compression for static and dynamic content to reduce bandwidth usage.
- Limit the number of worker processes in an application pool to avoid resource contention.
- Use output caching to store processed pages and serve them faster to users.
- Monitor server performance using tools like Performance Monitor to identify bottlenecks and optimize settings accordingly.
Security in Microsoft IIS
When it comes to hosting websites, security is of utmost importance. Microsoft IIS offers a range of built-in security features to help protect your web applications and data from potential threats. In addition to these features, you can further enhance security by using SSL certificates and implementing robust authentication methods. Here, we will explore the security measures you can take to secure websites hosted on Microsoft IIS.Built-in Security Features of Microsoft IIS
- Request Filtering: Allows you to control the types of requests that IIS will process, helping to prevent malicious requests.
- IP Address and Domain Restrictions: Enables you to restrict access to your website based on IP address or domain, enhancing security.
- Dynamic IP Restrictions: Helps protect against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks by dynamically blocking IP addresses that exhibit suspicious behavior.
Enhancing Security with SSL Certificates and Authentication
- SSL Certificates: By installing SSL certificates on your web server, you can encrypt data transmitted between the server and the client, ensuring data confidentiality.
- Authentication Methods: Implementing strong authentication methods such as Windows Authentication or Forms Authentication can help verify the identity of users accessing your website.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before granting access.
Best Practices for Securing Websites on Microsoft IIS
- Regularly Update Software: Keep your Microsoft IIS server up to date with the latest security patches and updates to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Use Strong Passwords: Encourage users to create strong, unique passwords and implement password policies to enforce password complexity.
- Enable Logging and Monitoring: Monitor server logs for suspicious activity and set up alerts to notify you of potential security breaches.
- Implement Secure Coding Practices: Follow secure coding practices to prevent common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Integration and Compatibility
When it comes to integration and compatibility, Microsoft IIS plays a crucial role in working seamlessly with other Microsoft products like ASP.NET and SQL Server. Let's delve into how this integration works and explore any compatibility issues that may arise.Integration with ASP.NET and SQL Server
- Microsoft IIS is specifically designed to work hand in hand with ASP.NET, Microsoft's web application framework. This integration allows for efficient hosting and running of ASP.NET applications on IIS servers.
- Additionally, Microsoft IIS can also integrate with SQL Server, Microsoft's relational database management system. This enables websites and applications hosted on IIS to interact with SQL Server databases seamlessly.
Compatibility with Different Versions of Windows and Microsoft IIS
- One of the key considerations when working with Microsoft IIS is ensuring compatibility with different versions of Windows. It is important to check the compatibility matrix provided by Microsoft to ensure that the version of IIS being used is supported on the Windows operating system in question.
- Similarly, compatibility between different versions of Microsoft IIS itself is crucial. Upgrading or migrating between versions should be done carefully to avoid any compatibility issues that may arise.
Troubleshooting Integration Problems with Third-Party Applications
- When integrating Microsoft IIS with third-party applications, issues may arise due to compatibility conflicts or configuration errors. To troubleshoot such problems, it is essential to carefully review the documentation provided by both the third-party application and Microsoft IIS.
- Common troubleshooting steps include checking configuration settings, ensuring proper permissions are set, and monitoring logs for any error messages that may provide insight into the issue.